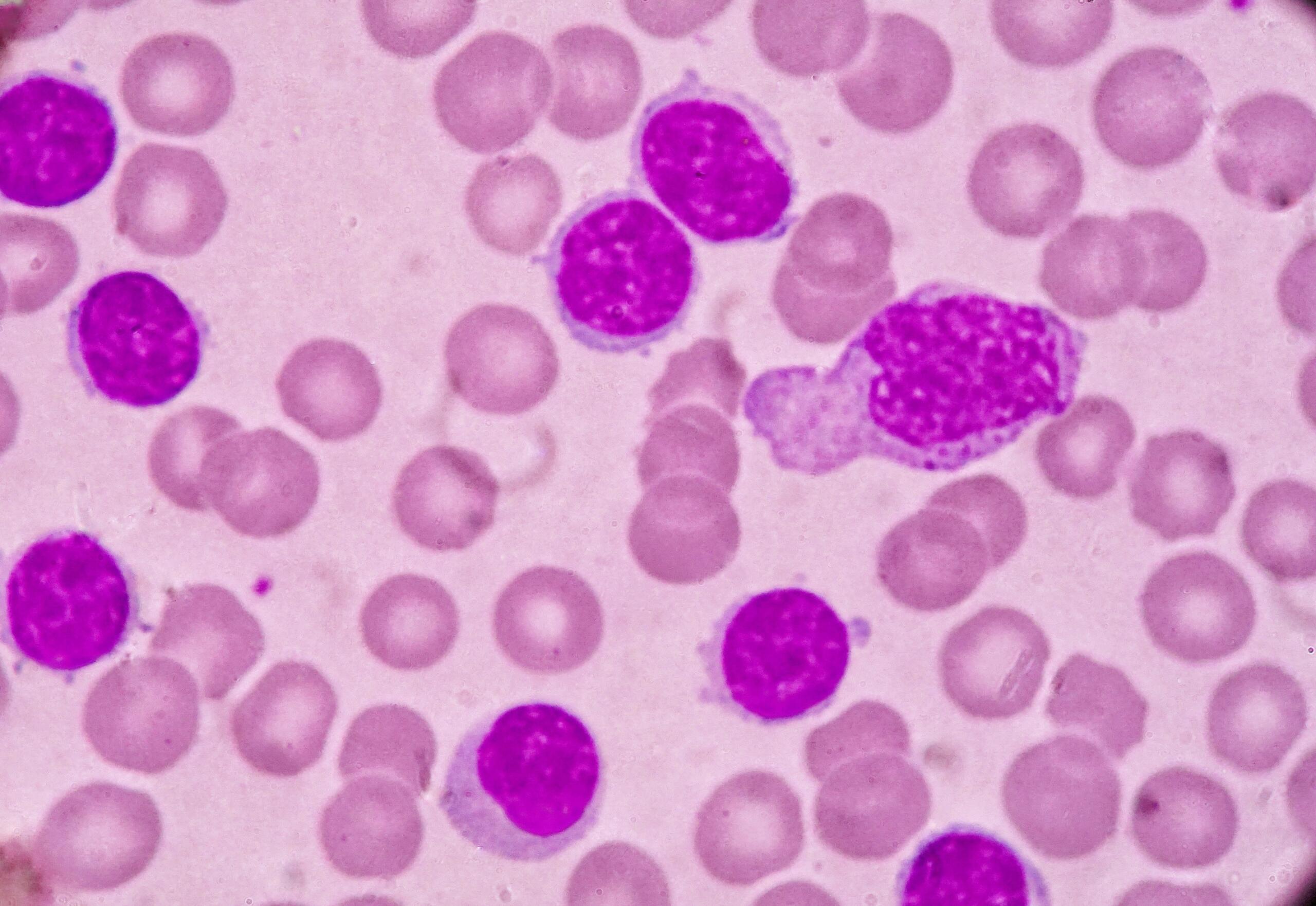
You’ve heard of leukemia, a type of blood cancer. But did you know that there are multiple types of leukemia – and that some are more concerning than others? Certain forms of leukemia like chronic lymphocytic leukemia might not capture very much attention, but they’re well worth knowing. These various and specific kinds of cancers can affect anyone, and if you don’t know the signs and symptoms, you can’t get treatment. Search online to learn more about chronic lymphocytic leukemia and its symptoms.
Though you may not have heard of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), it’s actually quite common. It’s the most common type of leukemia found in adults age 19 and older, and it makes up 37 percent of all leukemia cases. In order to catch CLL when it begins you need to be informed. Search online to learn more about this type of cancer.
What is Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a form of leukemia that begins in a particular set of cells. It forms in cells that will become white blood cells – specifically, lymphocytes – in your bone marrow.
Over time, the cancerous CLL-causing cells will build up in your bone marrow. This means you likely won’t notice any changes to your health. There won’t be any symptoms, and the cancer will grow unchecked. Ultimately, the lymphocytes will spread to other parts of the body. They can spread to the lymph nodes, liver, spleen, and other organs.
There are two types of CLL: one that grows very slowly over years, and one that progresses more rapidly. While slow-growing CLL has a better long-term outcome, both of these varieties of leukemia can be dangerous.
Are You at Risk?
Anyone can potentially develop CLL. Unfortunately, doctors don’t know what causes this common type of leukemia. And that leaves more questions than answers about who’s most at risk.
But doctors do know that certain risk factors can make you a more likely candidate for CLL. These factors include:
- Having a family member like a parent or sibling with CLL.
- Being middle-aged or older.
- Having relatives of Eastern European descent..
- Being a white man.
- Exposure to Agent Orange.
If you’re concerned about your potential risk factors for CLL, search online to find a specialist who can discuss your concerns. A doctor who’s familiar with CLL will be able to give you a solid assessment about your risk for developing this kind of leukemia.
Signs and Symptoms of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
The biggest problem with diagnosing CLL early is that a lack of symptoms is quite common. There are no real early symptoms – CLL typically shows no symptoms when it first begins, and it can go on growing for years with no obvious effects.
Once symptoms do begin, however, they can include:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Fatigue
- A fever
- Pain in the upper left side of the abdomen
- An enlarged spleen (which can cause abdominal pain)
- Night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Frequent infections.
If you’re concerned about potential changes to your health that may be a sign of CLL, it’s critical to see a doctor. Search online to find a doctor in your area who can perform the necessary diagnostic tests.
How Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia is Treated
If you are diagnosed with CLL, there are a number of different treatment options. The treatment options that are right for you will depend on some factors, like the stage of your cancer and any complications you might be experiencing.
Typically, treating CLL will involve treatment options like:
- Chemotherapy, which uses drugs to kill or control cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy, which uses drugs to help the immune system identify and kill cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy, which uses drugs to block proteins in and on cancer cells so they stop spreading.
- Radiation therapy, which uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.
- Surgery, which may be done to remove an enlarged spleen.
- Leukapheresis, which filters CLL cells out of your bloodstream.
If left untreated, CLL can lead to serious complications. It can affect your health in surprising ways, including:
- Frequent infections, particularly infections in the upper and lower respiratory tracts.
- Richter’s syndrome, which is a more aggressive type of cancer.
- An increased risk of developing other types of cancer.
- Problems with the immune system, which causes attacks on your own red blood cells or platelets.
Getting treatment means you need to see a doctor and get a diagnosis as soon as possible. In order to do that, you’ll have to keep a close eye on your health so you notice any changes. If you think you may be experiencing symptoms of CLL, make sure to see a doctor. You can search online to find local doctors who can perform the right diagnostic tests and give you answers to your questions.